Ducks are fascinating creatures with unique characteristics and adaptations that allow them to thrive in various aquatic environments. One question that often arises is whether ducks have ears, considering their water-dwelling lifestyle. This article delves into the anatomy of ducks and explores the presence and function of their auditory system.
In contrast to popular belief, ducks do indeed possess ears. However, unlike humans and many other animals with prominent external ears, ducks have specialized ear structures that are adapted to their aquatic environment.
While ducks lack visible, protruding ears, their auditory capabilities are remarkable. Let's explore the unique features of duck ears and how they contribute to their survival and interaction with the world around them.
Read also:Aubreigh Wyatt What Happened
Do Ducks Have Ears?
Despite lacking external ears, ducks possess unique auditory adaptations.
- Specialized ear structures
- Hidden ear openings
- Excellent hearing abilities
These features enable ducks to navigate their environment, communicate effectively, and detect potential threats.
Specialized ear structures
Ducks possess specialized ear structures that are adapted to their aquatic environment and unique hearing needs.
- Hidden ear openings:
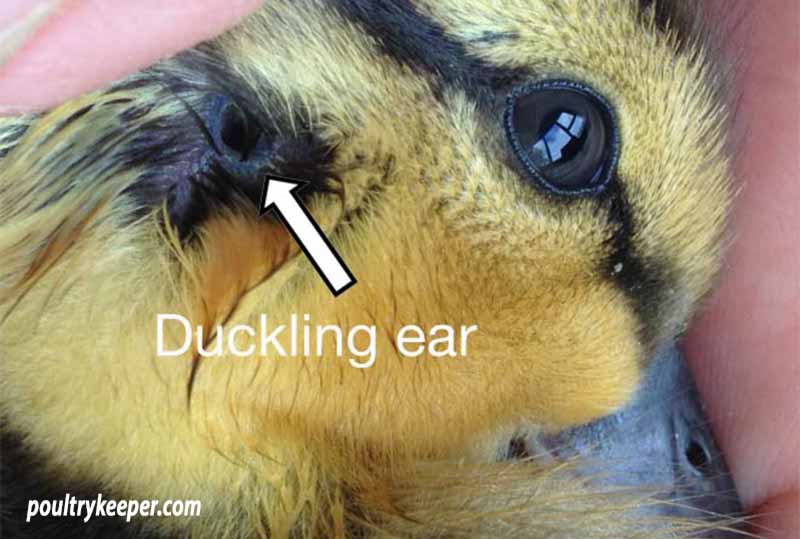
Unlike humans and many other animals, ducks' ear openings are not readily visible. These openings are small and hidden beneath their feathers, providing protection from water and debris while swimming and diving.
- External auditory canal:
Ducks have a short external auditory canal that leads from the ear opening to the middle ear. This canal is lined with specialized glands that produce a waxy substance, which helps prevent water from entering the ear.
- Tympanic membrane:
At the end of the external auditory canal is the tympanic membrane, also known as the eardrum. This thin membrane vibrates when sound waves reach it, transmitting these vibrations to the middle ear.
Read also:
- Cha Eun Woo Engagement Announcement What You Need To Know
- Middle ear and inner ear:
The middle ear and inner ear of ducks are similar to those of other vertebrates. The middle ear contains three small bones (the malleus, incus, and stapes) that amplify the vibrations from the tympanic membrane and transmit them to the inner ear. The inner ear contains fluid-filled chambers and sensory cells that convert these vibrations into electrical signals, which are then sent to the brain for interpretation.
These specialized ear structures allow ducks to hear a wide range of sounds, including high-pitched calls from other ducks, predators, and environmental cues such as the sound of running water or approaching storms.
Hidden ear openings
Ducks' hidden ear openings are a remarkable adaptation that allows them to thrive in their aquatic environments. These small, concealed openings are strategically positioned beneath their feathers, providing several benefits:
Protection from water: When ducks dive or swim underwater, their ear openings are effectively sealed, preventing water from entering the ear canal. This защищает delicate structures of the middle and inner ear from damage and infection.
Protection from debris: Ducks often forage in muddy or debris-filled waters. Their hidden ear openings help prevent dirt, sediment, and other particles from entering the ear canal, which could cause irritation or infection.
Streamlined swimming: The absence of prominent external ears reduces drag and allows ducks to swim more efficiently. This is particularly important for diving ducks, which propel themselves underwater using their powerful feet.
Cryptic coloration: The hidden ear openings contribute to the ducks' overall camouflage. By blending in with the surrounding feathers, the ear openings are less noticeable to predators, providing an element of protection.
In addition to these benefits, the hidden ear openings also help ducks to maintain their body temperature. The feathers surrounding the ear openings trap warm air, providing insulation and preventing heat loss, especially in cold or windy conditions.
Overall, the hidden ear openings of ducks are a testament to their remarkable adaptations for life in aquatic environments. These specialized structures protect the ears from water, debris, and cold temperatures, while also contributing to the ducks' streamlined swimming and cryptic coloration.
Excellent hearing abilities
Despite their hidden ear openings, ducks possess excellent hearing abilities that are well-suited to their aquatic lifestyle and communication needs. These abilities include:
Broad frequency range: Ducks can hear a wide range of frequencies, from low-pitched sounds below 100 Hz to high-pitched sounds above 10,000 Hz. This allows them to detect a variety of sounds in their environment, including the calls of other ducks, predators, and environmental cues.
Sensitivity to high-pitched sounds: Ducks are particularly sensitive to high-pitched sounds. This is likely an adaptation to their noisy environment, where they need to be able to hear each other's calls over the sound of waves, wind, and other ducks. Their sensitivity to high-pitched sounds also helps them detect predators, such as hawks and eagles, which often make high-pitched calls.
Directional hearing: Ducks have the ability to determine the direction from which a sound is coming. This is important for locating mates, avoiding predators, and navigating their environment. Their heads are shaped in a way that helps them funnel sound waves into their ears, allowing them to pinpoint the location of a sound source.
Acute underwater hearing: Some species of ducks, such as diving ducks, have specialized adaptations that allow them to hear underwater. Their ear openings can close tightly to prevent water from entering the ear canal, and their middle ear bones are modified to transmit sound waves effectively underwater.
The excellent hearing abilities of ducks are essential for their survival and communication. They allow ducks to navigate their environment, find food, avoid predators, and maintain social bonds with other ducks.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about ducks and their hearing abilities:
Question 1: Do ducks have ears?
Answer: Yes, ducks do have ears, but they are not visible like human ears. Their ear openings are small and hidden beneath their feathers.
Question 2: Where are ducks' ears located?
Answer: Ducks' ears are located on the sides of their heads, just behind and slightly below their eyes. The ear openings are small slits that are hidden by feathers.
Question 3: Can ducks hear?
Answer: Yes, ducks have excellent hearing abilities. They can hear a wide range of sounds, including high-pitched calls from other ducks, predators, and environmental cues.
Question 4: How do ducks hear underwater?
Answer: Some species of ducks, such as diving ducks, have specialized adaptations that allow them to hear underwater. Their ear openings can close tightly to prevent water from entering the ear canal, and their middle ear bones are modified to transmit sound waves effectively underwater.
Question 5: Why do ducks have hidden ear openings?
Answer: Ducks' hidden ear openings provide several benefits. They protect the ears from water and debris, help streamline the ducks' swimming, and contribute to their cryptic coloration.
Question 6: How do ducks use their hearing?
Answer: Ducks use their hearing for a variety of purposes, including communicating with each other, detecting predators, navigating their environment, and finding food.
Question 7: Can ducks hear humans?
Answer: Yes, ducks can hear humans. They are able to detect a wide range of sounds, including human voices. However, they may not always respond to humans in the same way that they respond to other ducks.
Closing Paragraph: Ducks' hearing is an important sense that helps them survive and thrive in their environment. Their specialized ear structures and excellent hearing abilities allow them to communicate effectively, detect predators, and navigate their surroundings.
In addition to their hearing abilities, ducks also possess a number of other adaptations that help them survive in their aquatic environment. These adaptations include waterproof feathers, webbed feet, and the ability to dive and swim underwater.
Tips
Here are a few tips for observing and understanding ducks and their hearing abilities:
Tip 1: Observe ducks in their natural habitat.
Visit a local pond, lake, or wetland area where ducks are known to congregate. Observe their behavior and listen for the sounds they make. Pay attention to how they communicate with each other and how they respond to different sounds in their environment.
Tip 2: Use binoculars or a spotting scope.
If you want to get a closer look at ducks' ears, you can use binoculars or a spotting scope. This will allow you to see the small ear openings hidden beneath their feathers. You may also be able to see ducks preening their ears, which is a sign that they are keeping them clean and healthy.
Tip 3: Listen for different duck calls.
Ducks have a variety of calls that they use to communicate with each other. These calls can vary depending on the species of duck, the situation, and the individual duck. Some common duck calls include quacks, peeps, whistles, and grunts. By learning to identify these calls, you can better understand how ducks communicate and interact with each other.
Tip 4: Be patient and respectful.
Ducks are wild animals, and it is important to be patient and respectful when observing them. Avoid making loud noises or sudden movements that could scare them away. Be mindful of your distance and give them plenty of space. Remember that ducks are sensitive to human presence, so it is important to observe them from a distance and avoid disturbing their natural behavior.
Closing Paragraph: By following these tips, you can learn more about ducks and their remarkable hearing abilities. Remember to be patient, respectful, and observant, and you will be rewarded with a fascinating glimpse into the world of these aquatic birds.
Ducks are fascinating creatures with a unique set of adaptations that allow them to thrive in their aquatic environment. Their hidden ear openings and excellent hearing abilities are just a few of the remarkable features that make them such successful survivors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, ducks do indeed have ears, despite the absence of visible external ears. Their specialized ear structures, including hidden ear openings, a short external auditory canal, and specialized middle and inner ear components, allow them to hear a wide range of sounds in their environment.
Ducks' excellent hearing abilities are essential for their survival and communication. They use their hearing to detect predators, find food, navigate their environment, and communicate with each other. Their sensitivity to high-pitched sounds and their ability to hear underwater are particularly noteworthy adaptations.
The hidden ear openings of ducks provide several benefits, including protection from water, debris, and cold temperatures, as well as streamlining their swimming and contributing to their cryptic coloration. These adaptations highlight the remarkable ways in which ducks have evolved to thrive in their aquatic habitats.
Overall, the unique ear structures and excellent hearing abilities of ducks are a testament to their remarkable adaptations for life in aquatic environments. These features allow them to navigate their surroundings, communicate effectively, and detect potential threats, ultimately contributing to their survival and success as a species.
Closing Message: The next time you see a duck swimming or flying overhead, take a moment to appreciate the remarkable adaptations that allow these fascinating creatures to thrive in their environment. Their hidden ears and excellent hearing abilities are just a few of the many features that make ducks such successful and resilient animals.